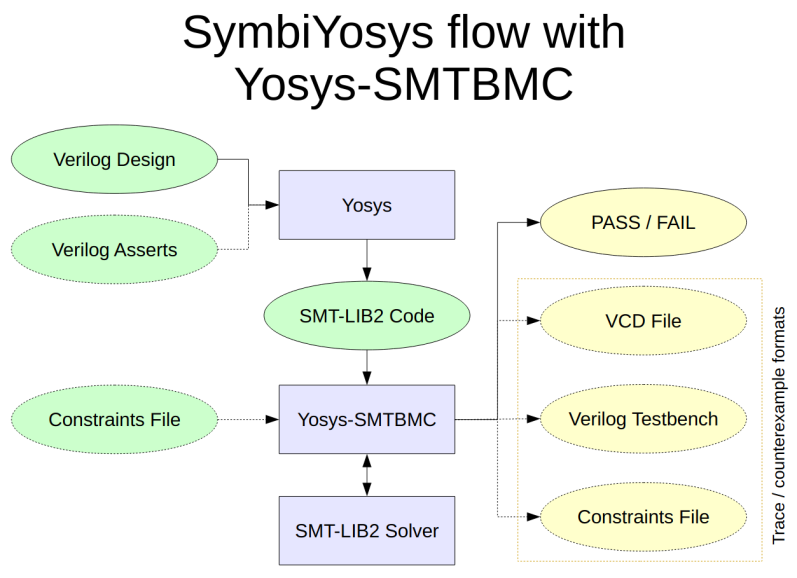
Yosys 是一个开源的 Verilog HDL 综合工具包。它支持将电路的状态转换编码为 SMT-LIBv2 中的函数。由此出发,可以对电路进行一系列形式化验证。
注意
本文仅对相关工具的一般使用方法进行介绍,不涉及验证原理、算法分析等内容。
本文讨论的内容均为 Assertion Based Verification (ABV),除此之外 Yosys 还支持 Symbolic Model Checking、Formal Equivalence Checking,相关用法有待进一步整理。
Motivating Example
test.v 定义了一个简单的时序逻辑电路(此示例电路来自 Yosys Command Reference Manual),它只有输出,没有输入。它的输出可以理解为一个数列 yn+1=or(shl(yn),neg(yn)),首项 y0 的值是电路的初始状态。
module test(input clk, output reg [3:0] y);
always @(posedge clk)
y <= (y << 1) | ^y;
endmodule我们的目标是验证输出 y 的值不可能从一个非零值变为一个零值。为了验证该性质,需要将其写为 SMT-LIBv2 表达式,交给 SMT solver 求解。因此,首先需要明白编码电路的方式。
使用以下综合脚本(synthesis script)test.ys 指示 Yosys 对电路进行变换,得到 test.smt2 文件。
# Read Verilog source file and convert to internal representation
.read_verilog test.v
# Elaborate the design hierarchy.
# Should always be the first command after reading the design.
hierarchy -check -top test
# Convert “processes” (the internal representation of behavioral Verilog code)
# into multiplexers and registers
.proc
# Perform some basic optimizations and cleanups
.opt
# Check for obvious problems in the design
.check -assert
# Write a SMT-LIBv2 description of the current design
.write_smt2 test.smt2理解 synthesis script
以上脚本包含了3种类型的指令:
Frontends:从文件中读取输入(一般为 Verilog 代码)
Passes:在电路上应用等价变换
Backends:将处理后的电路输出到文件(支持不同的格式,如 Verilog, BLIF, EDIF, SPICE, BTOR 等)
这也是所有典型的 Yosys synthesis script 都具有的结构,由此可见综合的过程与编译的过程非常相似。事实上,Yosys 定义了一种电路的中间表示格式 RTLIL (RTL Intermediate Language),所有的 Passes 都是在以此 IR 表示的抽象语法树(AST)上实现的。
1 $ yosys test.ys
Yosys 输出的文件如下。此文件中定义了一个对应电路状态的类型 |
SMT-LIBv2 description generated by Yosys 0.21+7 (git sha1 d98738db5, clang 10.0.0-4ubuntu1 -fPIC -Os);
yosys-smt2-module test(declare-sort |test_s| 0)(declare-fun |test_is| (|test_s|) Bool)(declare-fun |test#0| (|test_s|) Bool) ; \clk;
yosys-smt2-input clk 1;
yosys-smt2-clock clk posedge;
yosys-smt2-witness {"offset": 0, "path": ["\clk"], "smtname": "clk", "type": "posedge", "width": 1};
yosys-smt2-witness {"offset": 0, "path": ["\clk"], "smtname": "clk", "type": "input", "width": 1}(define-fun |test_n clk| ((state |test_s|)) Bool (|test#0| state));
yosys-smt2-witness {"offset": 0, "path": ["\y"], "smtname": 1, "type": "reg", "width": 4}(declare-fun |test#1| (|test_s|) (_ BitVec 4)) ; \y;
yosys-smt2-output y 4;
yosys-smt2-register y 4(define-fun |test_n y| ((state |test_s|)) (_ BitVec 4) (|test#1| state))(define-fun |test#2| ((state |test_s|)) Bool (xor (= ((_ extract 0 0) (|test#1| state)) #b1) (= ((_ extract 1 1) (|test#1| state)) #b1) (= ((_ extract 2 2) (|test#1| state)) #b1) (= ((_ extract 3 3) (|test#1| state)) #b1))) ;
$reduce_xor $test.v:3$3_Y(define-fun |test#3| ((state |test_s|)) (_ BitVec 4) (bvor (concat ((_ extract 2 0) (|test#1| state)) #b0) (concat #b000 (ite (|test#2| state) #b1 #b0)))) ;
$0\y3:0) Bool true)(define-fun |test_u| ((state |test_s|)) Bool true)(define-fun |test_i| ((state |test_s|)) Bool true)(define-fun |test_h| ((state |test_s|)) Bool true)(define-fun |test_t| ((state |test_s|) (next_state |test_s|)) Bool (= (|test#3| state) (|test#1| next_state)) ;
$procdff$5 \y) ;
end of module test;
yosys-smt2-topmod test;
end of yosys output
现在,为了表示上述性质,可以定义两个状态 s1, s2,它们满足:
1.s1 到 s2 存在状态转换关系
2.s1 中 y != 0
3.s2 中 y == 0
之后交给 SMT solver 验证其可满足性,若不能满足,则验证了不存在这样的情况。
we need QF_UFBV for this proof(set-logic QF_UFBV); insert the auto-generated code here%%;
declare two state variables s1 and s2(declare-fun s1 () test_s)(declare-fun s2 () test_s); state s2 is the successor of state s1(assert (test_t s1 s2)); we are looking for a model with y non-zero in s1(assert (distinct (|test_n y| s1) #b0000));
we are looking for a model with y zero in s2(assert (= (|test_n y| s2) #b0000));
is there such a model?(check-sat)
将上面的 test.ys 最后一行修改为:
1 write_smt2 -tpl test.tpl test.smt2
新的输出文件中包含了模版文件 test.tpl 的内容,并将其中的 %% 替换为了原本 write_smt2 命令的输出,可以将它作为 SMT solver 的输入。
例如,调用 z3 进行求解,得到 unsat 的结果。
12 $ z3 test.smt2unsat
使用 SymbiYosys 进行验证
上一节介绍的方法需要用户理解 write_smt2 命令的输出,并直接使用其中定义的函数,才能将需要验证的性质编写为 SMT-LIBv2 格式的表达式,这样不免有些繁琐。Yosys 还提供了 SymbiYosys (sby) 工具,它可以理解为一个前端驱动程序(front-end driver program),支持解析用户在源文件中定义的断言(assertions),直接尝试进行证明。
来看另一个例子,下面是用 System Verilog 定义的一个计数器(此示例代码来自参考资料中 Formal Verification of RISC-V cores with riscv-formal 这一幻灯片的第3~4页)。
module hello ( input clk, rst, output [3:0] cnt);
reg [3:0] cnt = 0;
always @(posedge clk) begin
if (rst)
cnt <= 0;
else
cnt <= cnt + 1;
endendmodule现在来定义此电路需要满足的性质。首先用1个 assume 语句表明验证的前提(也就是在求解器考虑的所有情形中,此性质都得到满足);assert 语句则是求解器需要证明的性质。
module hello (/* ... */);/* ... */
`ifdef FORMAL
always @*
assume (cnt != 10);
always @*
assert (cnt != 15);
`endif
endmoduleSymbiYosys 使用一个 .sby 文件来描述验证过程中执行的任务,文件中包含若干个节(section),每个节由方括号括起的小标题表示。下面的文件中,[options] 节将证明模式设置为“使用 Unbounded model check 验证 safety properties”,并且将 k-induction 的深度设置为10;[script] 中是处理输入文件用到的 Yosys 命令;输入文件列在 [files] 节中。关于 .sby 文件语法的更多信息请参考 Reference for .sby file format,这里并不展开说明。
mode provedepth 10[engines]
smtbmc z3[script]
read_verilog -formal hello.sv
prep -top hello[files]
hello.sv将上面的两个文件放在同一目录下,然后调用 sby 程序,即可获得证明结果。
$ sby -f hello.sby...SBY 19:06:39
[hello] engine_0.induction: finished (returncode=0)SBY 19:06:39
[hello] engine_0: Status returned by engine for induction: pass...SBY 19:06:39
[hello] engine_0.basecase: finished (returncode=0)SBY 19:06:39
[hello] engine_0: Status returned by engine for basecase: passSBY 19:06:39 [hello] summary: Elapsed clock time [H:MM:SS (secs)]: 0:00:00 (0)SBY 19:06:39
[hello] summary: Elapsed process time [H:MM:SS (secs)]: 0:00:00 (0)SBY 19:06:39
[hello] summary: engine_0 (smtbmc z3) returned pass for inductionSBY 19:06:39
[hello] summary: engine_0 (smtbmc z3) returned pass for basecaseSBY 19:06:39
[hello] summary: successful proof by k-induction.SBY 19:06:39 [hello] DONE (PASS, rc=0)

评论 (0)